PLTU Labuan — Thermal Power Generation
Comprehensive root cause analysis, numerical simulation, and Fitness-for-Service assessment to address HP Heater leakage, derating, and long-term operational integrity.

High Pressure (HP) Heaters play a critical role in thermal efficiency and reliability of steam power plants. Leakage and degradation in HP Heaters can directly lead to system derating, reduced efficiency, and increased risk of forced outages.
This project focused on investigating the impact of HP Heater leakage on plant load reduction, identifying root causes of failure, and developing engineering-based design and operational recommendations using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) and Finite Element Analysis (FEA).
The study was conducted through integrated numerical simulation and Fitness-for-Service assessment, providing a data-backed foundation for strategic decisions on component redesign and operational limits.
The HP Heater experienced leakage that resulted in critical operational issues:
Decreased heat transfer effectiveness impacting thermal efficiency
Thermal cycling causing localized overheating in critical zones
Elevated stress levels on tubes and shell components
Overall power plant output reduction due to HP Heater limitations
The client required a clear, data-driven understanding of failure mechanisms and engineering justification for corrective actions.
Identify the root cause of HP Heater leakage and derating
Verify structural integrity and remaining life of critical components
Evaluate thermo-fluid and mechanical behavior using CFD and FEA
Perform Fitness-for-Service Level 3 assessment for remaining life
Develop design and mitigation recommendations to restore reliability
Comprehensive data collection and onsite inspection:
Computational Fluid Dynamics simulations to analyze:
FEA was applied to evaluate structural integrity:
Level 3 FFS assessment covering:
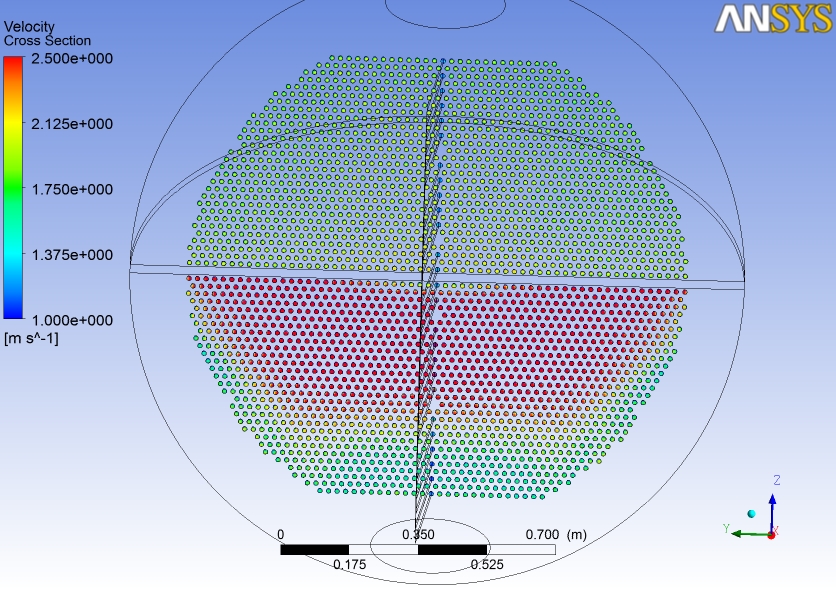
CFD Analysis: High turbulence and secondary flow at tube U-bends identified. Local velocity exceeding 2.4 m/s triggering thermal cycling.
Tube Side Assessment: Tube side stress exceeded allowable limits — design modification required.
Shell Side Assessment: Shell side stress remained within allowable limits — structurally acceptable.
Design Solution: Increasing tube thickness (ANSI/ASME STD 40/40S to XS 80/80S) significantly improved safety factors.
HP Heater derating was driven by thermal-fluid induced stress concentration, not solely material degradation. Tube U-bend regions were identified as the most critical zones requiring design modification.
CFD simulation results, FEA stress analysis, and thermal distribution outputs from the HP Heater study.
Garuda Engineering delivers advanced failure analysis and life assessment through proven expertise and rigorous methodology.
"We transform complex failure mechanisms into actionable engineering solutions."
Experiencing recurring HP Heater issues or plant derating? Contact Garuda Engineering for a comprehensive Failure Analysis & FFS Study.