PLTU Labuan 300 MW
Computational aerothermodynamics analysis to evaluate burner geometry, combustion behavior, and thermal distribution in a large-scale coal-fired furnace.

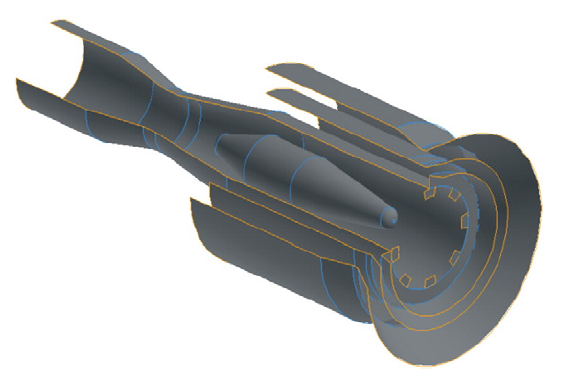
Coal burner geometry plays a critical role in combustion stability, temperature distribution, and emission formation within a power plant furnace.
This project focused on a Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) aerothermodynamics study of coal burners at PLTU Labuan 300 MW, comparing circular and rectangular burner configurations under identical operating conditions.
The objective was to understand how burner geometry influences flame development, temperature distribution, combustion location, and NOx formation potential.
The existing burner configuration raised several operational concerns:
Non-uniform temperature distribution inside the furnace
High local flame temperature contributing to NOx formation
Combustion occurring too close to furnace walls
Limited flexibility for emission optimization
Compare aerothermodynamic behavior of circular and rectangular burner designs
Evaluate temperature and velocity distribution inside the furnace
Identify combustion location relative to furnace axis and walls
Assess implications for NOx reduction and combustion stability
Temperature Distribution: Circular burner produced lower exit temperature compared to rectangular burner, reducing thermal NOx formation potential.
Combustion Behavior: Circular burner combustion was more centralized, similar to full-furnace behavior. Rectangular burner showed wider spread toward walls.
Velocity & Flow Pattern: Circular burner generated more uniform swirling flow with improved flame stability and mixing characteristics.
Conclusion: Original circular burner geometry provides superior combustion control and supports NOx reduction strategies.
The study confirms that burner geometry optimization is a powerful tool for improving combustion quality and emissions without major hardware changes.
CFD simulation results, temperature contours, velocity fields, and burner geometry comparisons.
Garuda Engineering delivers advanced combustion insight through proven expertise and rigorous methodology.
"We convert numerical flow fields into practical combustion solutions."
Looking to improve combustion efficiency or reduce emissions through burner optimization? Contact Garuda Engineering for an aerothermodynamics study.